The world of digital marketing is in the midst of a significant shift as third-party cookies are coming to an end. This change will have far-reaching implications for businesses that rely on these cookies to track user behaviour and gather data for advertising purposes.
With the loss of third-party cookies, businesses will need to find new ways to reach and engage with their audiences. They will also need to focus on collecting more first-party data directly from their own website or app, building stronger relationships with their customers and gaining explicit consent from them.
In this blog post, we will explore the potential impacts of the end of third-party cookies on digital marketing and discuss how businesses can adapt to these changes to succeed in the evolving landscape.

Impact on Measurement and Attribution
The loss of 3rd party cookies will make it more difficult for businesses to accurately measure and attribute marketing campaigns. This means that businesses will need to rely more on alternative measurement methods, such as attribution modelling and first-party data, to understand the impact of their marketing efforts.
Changes in Advertising Models
Third-party cookies have been widely used in digital advertising to track user behaviour and provide targeted ads. Without 3rd party cookies, businesses will need to find new ways to reach and target audiences. This may result in a shift towards contextual advertising, where ads are placed based on the content of the website being viewed, rather than the individual user’s behaviour.
More Focus on First-Party Data
With the loss of third-party cookies, businesses will need to rely more on their first-party data, such as data collected from their own website or app. This means that businesses will need to focus on building direct relationships with their customers and collecting data through their own channels.
A Fragmented Online Buyer Journey
The buyer’s journey is the process that a potential customer goes through when making a purchasing decision. It is a series of steps that a buyer takes, starting from the moment they realise they have a need or a problem that needs to be solved, all the way through to the final decision of purchasing a product or service.
Ad platforms like Google and Facebook have been using third-party cookies to track users’ online activities across different websites and apps. This enabled them to create interest-based audience groups and categorise people into distinct stages of the buyer journey, allowing advertisers to design campaigns and tailor ads accordingly. This has allowed highly sophisticated targeting, as well as optimisation of bids and tailored ad copy.
However, with the increasing use of cookie-blocking devices and companies such as Apple disabling app tracking by default, creating a buyer funnel for targeting and bid optimisation is becoming more challenging for ad platforms. To address this issue, the solution is to utilise first-party data such as server events, first-party encryption, or CRM lifecycle changes.
The Buyer Funnel Tracking
Relying solely on advertising platforms like Google and Facebook to build an online funnel of buyer behaviour as people browse the internet is no longer as effective as it used to be.
In today’s competitive landscape, it is crucial to employ a range of newer techniques to retain your marketing results and stay ahead of the competition. This blog post aims to provide you with the best solutions to ensure you maximise the value of your advertising efforts. First, let’s take a look at what the buyers funnel is and how it is used is advertising online and offline.
The Buyers Funnel Explained
Buyer funnels have always existed, predating Internet marketing. Traditional advertising models still hold true today, supported by data. The funnel consists of three phases: awareness, consideration, and decision/conversion. Awareness captures attention, consideration involves evaluating options, and the decision phase leads to conversion. While the digital landscape has introduced new touchpoints, the principles of the buyer’s funnel remain crucial. Understanding and leveraging this concept helps guide potential customers towards conversion.
Awareness: This is the stage where the buyer realises, they have a problem or a need that needs to be addressed. They start researching and exploring different options to solve their problem.
Consideration: In this stage, the buyer has a better understanding of their options and is evaluating the different solutions available. They are comparing products or services and consider their benefits and drawbacks.
Decision: This is the final stage where the buyer has made a decision on which product or service to purchase. They may also be considering factors such as price, delivery, and post-purchase support.
Understanding the buyer’s journey is crucial for businesses to effectively market their products and services. By identifying where a potential customer is in the buyer’s journey, businesses can tailor their messaging and content to address the customer’s specific needs and concerns at each stage through lead nurturing, leading to a successful sale.
As online tracking methods evolve, it is crucial to adapt your strategies to maximise marketing effectiveness. One effective approach is to synchronize your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system with ad platforms like Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn which allow for better optimisation of your ad account through enhanced bidding strategies, more accurate reporting, and increased efficiency..
By synchronizing your CRM with ad platforms like Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn, you can significantly improve your advertising return on investment (ROI). This integration allows for full-funnel marketing optimisation by aligning your CRM data with advertising platforms, letting you create more targeted and personalised campaigns that cater to each stage of the buyer’s journey.
This approach enables By leveraging the valuable customer data stored in your CRM, you can make informed decisions, target the right audience, and allocate your advertising budget more effectively. Ultimately, this integration leads to improved ROI and better overall performance of your advertising campaigns.

Increased Importance of Consent and Privacy
Without the ability to track user behaviour across the web, businesses will need to rely on users’ consent to collect data. This means that businesses will need to be more transparent about their data collection and usage practices and provide clear options for users to opt in or out of data collection.
The impact of GDPR on Digital Marketing
GDPR & Cookies
The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) recommends that cookie banners should be set up to reject non-essential cookies by default. This means that when users visit a website, they are not automatically tracked by cookies that are not strictly necessary for the website’s basic functionality.
Many companies are following this recommendation and have started using cookie banners that reject third-party advertising and analytics cookie tracking by default. In some cases, these scripts are deferred from loading until the user has actively consented to the use of cookies through the banner.
The use of cookie banners has become increasingly important in light of data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. These regulations require websites to obtain users’ explicit consent for the use of cookies and provide them with clear and comprehensive information about the cookies used on the site.
In addition to cookie banners, some websites are also implementing other privacy-enhancing measures, such as implementing a “do not track” feature or providing users with the ability to opt-out of specific types of cookie tracking. As companies continue to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and user expectations, we may see further changes to the way cookies are used and managed on the web.
GDPR & Email
Under the GDPR, companies must obtain opt-in consent from individuals before sending them marketing emails. This means that companies cannot simply assume that individuals are willing to receive marketing emails unless they have explicitly given consent.
To obtain valid consent, companies must clearly and transparently explain the purpose and nature of the marketing emails they plan to send. They must provide specific information about the type of content that the individual can expect to receive, the frequency of emails, and any other relevant details about the marketing campaign.
Under the GDPR, companies must obtain opt-in consent from individuals before sending them marketing emails. This means that companies cannot simply assume that individuals are willing to receive marketing emails unless they have explicitly given consent.

Google Analytics 4 Tracking
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is designed to emphasise first-party tracking rather than third-party tracking. GA4 includes new features that enable businesses to collect first-party data directly from their own website or app using server event tracking instead of traditional third-party cookies.
This shift towards first-party tracking aligns with the growing emphasis on user privacy and data protection. By relying on first-party data, businesses can build better relationships with their customers and offer greater transparency and control over their data.
Furthermore, GA4’s machine learning capabilities can analyse the data collected from first-party sources and provide insights that can be used to improve marketing strategies and customer engagement.
In conclusion, GA4 is designed to support first-party tracking, which allows businesses to collect data directly from their own website or app. This aligns with the trend towards user privacy and data protection and provides an opportunity for businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers.
Google Chrome Tracking
Google Chrome, the most popular web browser globally, will soon stop supporting third-party cookies. This will make it harder for businesses to track user behaviour and gather data for advertising purposes. Additionally, many apps will also have reduced tracking abilities, making it even more challenging for digital marketers to collect data.
Google’s strategy to phase out third-party cookies in Chrome is aimed at creating a privacy sandbox that uses open standards to track users while ensuring their privacy. However, this strategy has been facing challenges in the form of antitrust investigations from the European Commission, among others.
The privacy sandbox is a platform developed by Google to promote a more privacy-focused online experience. It includes APIs that enable advertisers to target users based on general interest categories without revealing their individual identities. The privacy sandbox can also be used for measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns while preserving users’ privacy.
While the privacy sandbox aims to improve online privacy, it has been met with resistance and scrutiny. The EU Commission has launched antitrust investigations into Google’s advertising practices, including the privacy sandbox, to ensure that they are not anti-competitive. Google has maintained that the privacy sandbox is intended to protect user privacy while supporting the advertising industry.
For more information on Google’s privacy sandbox, visit the website https://privacysandbox.com/.
Google Display Targeting & Tracking
As the phasing out of third-party cookies progresses, Google is expected to make changes to the targeting methods used for its Display and YouTube advertising platforms. One such change includes the end-of-life of Similar Audiences, which has already been announced by Google [source].
The impact of these changes may also extend to Google Search, as Display targeting audiences are often layered upon Search campaigns. This could potentially affect smart bidding strategies as well. As Google continues to prioritise user privacy, it’s possible that further adjustments and updates to its advertising practices will be made in the future.
Facebook Advertising & Cookies
Already with the release of Apple’s iOS14 update, there have been significant changes to Facebook Ads tracking. (And other social media platforms like TikTok, Twitter etc).
One of the most notable changes is the introduction of App Tracking Transparency (ATT), which requires apps to obtain user consent before tracking their activity across other apps and websites. This has resulted in challenges for Facebook Ads tracking, as many iOS users are now choosing to opt out of tracking.
The end of third-party cookies will have a further impact on Facebook Ads tracking, which uses third-party cookies to track user behaviour across multiple websites and platforms and are a key tool in measuring the effectiveness of ad campaigns. With the phasing out of third-party cookies, businesses will no longer be able to rely on this technology to track user activity. This means that Facebook Ads tracking will need to rely on other methods to gather data on user behaviour, such as first-party cookies and other tracking technologies.
In anticipation of the end of third-party cookies, Facebook has introduced new tracking tools and features, including the Conversions API. This API enables businesses to track website events as first-party data and to include first-party user data that is hashed and encrypted to ensure user privacy. By collecting data as first-party data, Facebook can ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data while maintaining the privacy of users.
The Conversions API also allows businesses to upload offline data, such as customer information and purchase data, to Facebook. This allows for more accurate measurement and targeting of ad campaigns and can help businesses to better understand the impact of their ads on offline purchases.
Overall, while the end of third-party cookies will present some challenges for Facebook Ads tracking, businesses are taking steps to adapt and ensure that effective tracking and measurement of ad campaigns can continue in the post-cookie era, which we discuss in more detail below.
1st Party Data Tracking - In-Depth
The end of third-party cookies and the reduction in app tracking abilities will require businesses to adjust and find alternative methods to collect data for advertising. Relying on first-party data from their website or app will become more important in digital marketing and is the future replacement for ad tracking. This provides an opportunity for businesses to establish better relationships with their customers while prioritising privacy and transparency.
By utilising first-party data, businesses can improve their marketing strategies and maintain a comprehensive view of their customers. Moreover, this approach is more privacy-focused, as users provide their data directly to the business instead of being tracked across the web. By using first-party data, companies can offer better transparency and control to users, thereby enhancing the user experience.
Using a CRM to replace Third Party Cookie Tracking
Digital marketing will also rely more on CRM systems that integrate both online and offline activities to attribute leads to sales. Now that you are capturing more first-party data like email addresses, you can utilise lead nurturing capabilities like email marketing to move prospects through the buyer funnel.
Integration of CRM with Ad Platforms
Linking offline CRM conversions with advertising systems such as Google, Facebook, and LinkedIn are also becoming more widely practised, and an opportunity to strive ahead of the pack as 3rd party cookies fade away.
Integration of a CRM system to advertising platforms such as Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads can provide a range of benefits to companies advertising in the first-party tracking era including:
Improved Targeting:
Integrating CRM data with advertising platforms can help businesses create highly targeted ads by segmenting their audience based on demographics, interests, behaviours, and other relevant attributes. This approach allows businesses to deliver more personalised ads to the most appropriate audience.
For instance, companies can use first-party IP addresses to identify company names of website visitors and retarget their employees on LinkedIn by combining company list targeting on LinkedIn with contact targeting, including job title demographics. Alternatively, businesses can use Customer Match lists on Google Ads or Facebook Ads to build an ideal customer profile (ICP) for better targeting. By leveraging these strategies, businesses can enhance their advertising efforts and maximise their return on investment.
Enhanced Personalisation:
By utilising CRM data, businesses can personalise their ads and messaging by creating contact, company and website visitor lists, making them more compelling and relevant to the individual user. Personalisation and segmentation can increase engagement and conversions and help build stronger relationships with customers.
Optimised Bidding:
Integrating a CRM system with advertising platforms enables businesses to enhance their bidding strategies and maximise their advertising budget. By utilising CRM data, businesses can identify high-value customers and adjust their bids accordingly, ensuring that they get the most out of their advertising expenditure.
For instance, businesses can update advertising platforms such as Google with changes to lead lifecycle stages as prospects move through the buying funnel in your CRM system. This approach allows businesses to optimise their bidding strategies based on the most up-to-date information about their leads and customers.
It’s essential to remember that not all leads are created equal, and simply optimising for Cost Per Lead (CPA) might not result in the best return on investment (ROI). To maximise ROI, businesses can send the sale value data back to Google Ads or Facebook, allowing them to optimise for Cost Per Sale or even Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), instead of just CPA.
By training the bidding AI to prioritise the acquisition of customers, rather than just leads, businesses can increase their chances of generating sales and revenue. This approach allows the AI to learn and adjust its bidding strategies based on the most profitable actions for the business, ultimately resulting in a better ROI for the advertising spend.
By linking their CRM system to advertising platforms, businesses can gain deeper insights into their customers and enhance their advertising efforts. This approach not only optimises their bidding strategies but also improves their overall return on investment.
Improved Attribution:
By linking CRM data to advertising platforms, businesses can better understand the impact of their advertising campaigns on customer behaviour. They can track customer interactions across multiple channels, attribute conversions to specific ads or campaigns, and see which leads become customers.
Want to learn more about using a CRM for advertising and offline Conversion tracking?
Using a CRM System to be GDPR Compliant
Using a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can be an effective way to demonstrate GDPR compliance. Here are some ways a CRM can help:
Data Inventory:
A CRM system can help keep track of all personal data collected by the company, how it is processed, and where it is stored. This helps identify which data needs to be protected and to what extent.
Consent Management:
A CRM can be used to record and manage individual consent to data processing. It can provide an audit trail of how and when consent was obtained and make sure that individuals’ rights to revoke consent are respected.
Data Access:
A CRM can be configured to grant and restrict access to personal data based on specific roles and responsibilities. This ensures that only authorised individuals have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of unauthorised access and data breaches.
Automated Reporting:
A CRM can be used to generate reports automatically to monitor compliance with GDPR regulations, such as consent rates and data breaches. These reports can be used to identify areas that need improvement and track progress towards GDPR compliance.
Data Retention:
A CRM can be used to set up retention policies to ensure that personal data is not kept for longer than necessary. It can also facilitate the deletion of data after a specified period of time or when requested by the individual.
Training Records:
A CRM can be used to record and track GDPR training provided to employees. This ensures that all employees are aware of their responsibilities under GDPR and helps identify any gaps in knowledge.
However, it is important to note that a CRM alone cannot guarantee GDPR compliance. It should be used in conjunction with other policies, procedures, and tools to ensure that all aspects of data protection and management are addressed.

Industries & Verticals:
For service-based companies, synchronizing changes in the lead lifecycle in your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system with Google Ads, Facebook Ads or LinkedIn Ads is an effective way to optimise your advertising efforts.
As leads progress through the sales process, your CRM can update Google Ads accordingly with your buyer funnel, allowing you to make more informed decisions and maximise your ROI.
Similarly, for e-commerce companies, utilising a CRM system to record sales from paid ads that were not originally recorded online can improve the accuracy of your conversion data. By feeding this data back into your ad platform, you can gain a better understanding of the effectiveness of your advertising efforts and make more informed decisions about where to allocate your resources.
1st Party Tracking: Server Events & Data Encryption
Instead of tracking from the browser with a cookie, a company can set up server-side user event tracking and user newer tracking approaches to record 1st party data.
Google already provide this as an alternative to standard tracking scripts such as Google Ads or Google Tag Manager.
Google’s Server Tag Manager is already being used by some companies instead of traditional third-party cookies in Google Ads. This approach to tracking is expected to replace web cookies in the near future.
In the case of Facebook Ads, running server event tracking and cookie tracking concurrently. Facebook deduplicates the two sources and then deletes any server events where a corresponding cookie event exists.
Additionally, Google Ads Enhanced Conversion Tracking enables companies to capture both first-party and traditional third-party cookie data. Enhanced conversion tracking is a feature in Google Ads that allows for more accurate measurement of conversions by supplementing existing conversion tag data with additional data. Enhanced conversion tracking can capture a variety of first-party data, including emails and phone numbers.
Enhanced conversion and server event tracking involves sending hashed first-party conversion data from a website to Google through hash encryption This data is captured in conversion tracking tags and then hashed before being sent to Google.
The enhanced conversion tags can then send the hashed data directly to a CRM or offline lead management system, where it can be traced back to Google Ads users to track conversion actions that took place, allowing for more accurate conversion tracking and attribution to improve advertising ROI.
This helps companies gather more comprehensive data to better understand their customer’s behaviour and improve their digital marketing strategies. Companies can also gain more insights into their customers’ journeys from ad impression to conversion, helping them identify which campaigns are most effective in driving sales.
Tracking for E-commerce websites
Offline conversion tracking for e-commerce refers to the process of tracking and attributing conversions that occur offline, such as purchases made in physical stores or over the phone, to online marketing campaigns. You can also record any missing transactions that occurred online, but were not recorded by the ad platform like Google or Facebook. So, by implementing offline conversion tracking, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the impact your online ads have on offline sales.
Using Zapier with E-commerce Websites
Zapier is a platform that allows you to automate workflows by connecting different apps and services together. To set up offline conversion tracking for Google Ads and Facebook Ads using Zapier, you can integrate your website with ad platforms, you’ll need to follow a few steps:
1. Connect Google Ads and Facebook Ads with Zapier:
Sign up for a Zapier account and connect your Google Ads and Facebook Ads accounts to it. This will enable Zapier to access the necessary data for tracking conversions.
2. Set up trigger events:
In Zapier, create a trigger event that listens for specific actions, such as a purchase confirmation or lead form submission, in your e-commerce system. This trigger event will initiate the tracking process when an offline conversion occurs.
3. Capture conversion data:
When the trigger event is activated, Zapier will collect relevant conversion data, such as order IDs, customer information, and purchase details, from your e-commerce system.
4. Format the data:
Convert the collected data into a format that can be recognized by Google Ads and Facebook Ads. Each platform has its own requirements for offline conversion data formatting.
5. Send data to Google Ads and Facebook Ads:
Use Zapier to send the formatted conversion data to Google Ads and Facebook Ads. This process involves creating actions or triggers that deliver the data to the respective platforms.
6. Match conversions with ad campaigns:
To accurately attribute offline conversions to specific ad campaigns, you need to match the conversion data with the corresponding campaigns in Google Ads and Facebook Ads. This typically involves using unique identifiers or tracking parameters to connect the offline conversions with online ads.
7. Track and analyze results:
Once the setup is complete, offline conversions will be tracked and attributed to your online campaigns. You can monitor these conversions within the Google Ads and Facebook Ads interfaces, allowing you to assess the effectiveness of your advertising efforts.
It’s worth noting that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the e-commerce platform, CRM, and other tools you use. Zapier offers a wide range of integrations, so you may need to explore their documentation and available options to find the best workflow for your specific setup.
Shopify & Offline Conversions
Integrating Shopify with Zapier not only enables you to automate processes and data transfers but also provides the opportunity to record sales with their click IDs and send them back to advertising platforms like Google Ads or Facebook Ads as conversions. This functionality allows for a more comprehensive tracking and optimisation of your online marketing campaigns.
Here’s a closer look at how this integration can help with click ID tracking and conversion attribution:
1. Click ID Tracking:
When a user clicks on an advertisement, they are often assigned a unique identifier known as a click ID. This click ID is typically provided by the advertising platform and serves as a reference point to track the user’s journey from the ad click to the final conversion.
2. Shopify and Zapier Integration:
By integrating Shopify with Zapier, you can capture the click ID information when a customer makes a purchase in your Shopify store. This integration allows you to access and work with the click ID data within your automation workflows.
3. Automating Click ID Transfer:
With the help of Zapier, you can automate the transfer of click ID data from Shopify to the advertising platforms where you’re running your campaigns, such as Google Ads or Facebook Ads. This ensures that the click ID associated with each sale is recorded and available for conversion tracking.
4. Conversion Attribution:
Once the click ID data is sent back to the advertising platforms, it becomes possible to attribute conversions accurately to the corresponding ad clicks. This enables you to measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and optimise them based on the actual sales generated.
5. Marketing Campaign Optimisation:
Armed with the conversion data that includes the click ID, you can make data-driven decisions to optimise your marketing campaigns. For example, you can identify which specific ads or keywords are driving the most valuable conversions, allowing you to allocate your budget more effectively and refine your targeting strategies.
By integrating Shopify with Zapier, you streamline the process of recording click ID data and ensure accurate conversion attribution within your advertising platforms. This enhanced tracking capability empowers you to make more informed decisions about your marketing efforts, improving the overall performance and return on investment of your online campaigns.
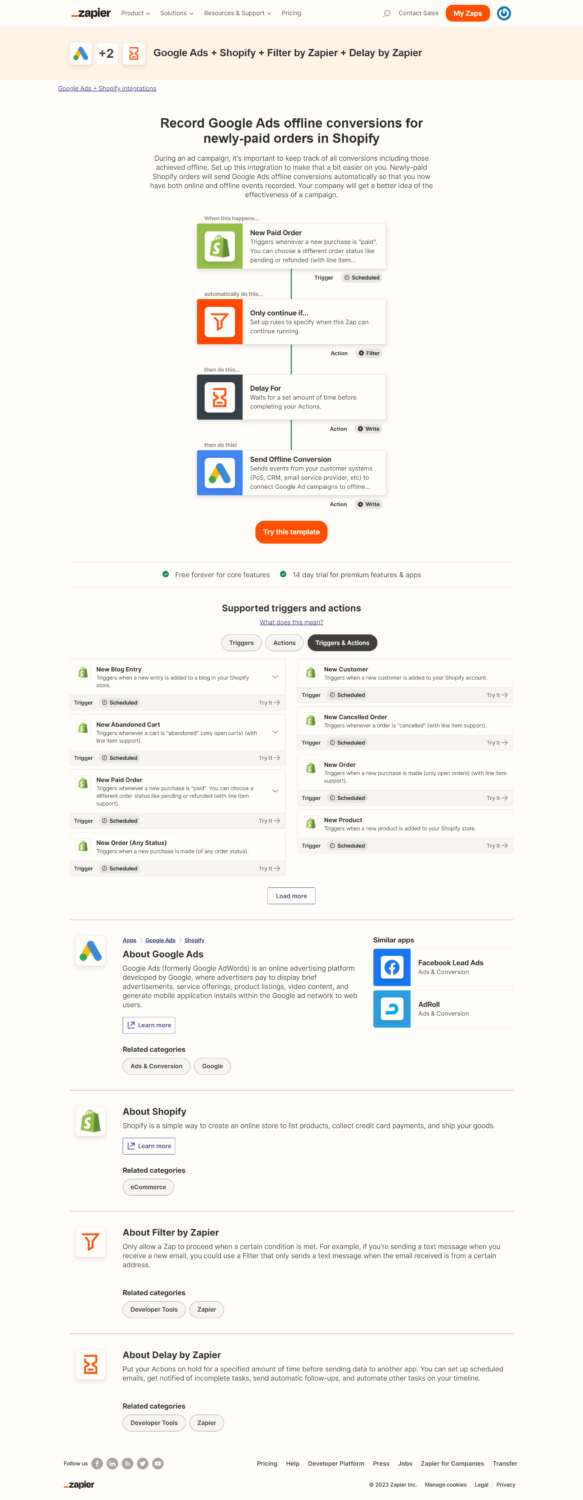
Technical tracking Explanation for CRM & Ad platforms
If you record the click ID in your CRM system, you can even use this in the same way offline conversion tracking complements online tracking for conversions that are not recorded online. (Like a catch-all).
By recording the advertising click ID in your CRM system, you can complement online tracking and capture conversions that may not be recorded online due to changes in 3rd party tracking in say Google Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Analytics etc.
The advertiser can then use it in the same way that offline conversions are currently recorded and attributed to your online advertising efforts. This approach helps to create a more comprehensive view of your customer’s journey, from initial click to final sale and enables you to accurately measure the effectiveness of your digital marketing campaigns.
Overall, integrating a CRM system with advertising platforms can help businesses maximise the ROI of their advertising efforts. It allows them to better understand their customers, target them more effectively, and deliver more personalised and relevant messaging.

Potential for Innovation and Disruption
The end of 3rd party cookies presents an opportunity for innovation and disruption in the digital marketing industry. Businesses will need to find new ways to reach and engage with audiences, and this may result in the development of new technologies and approaches.
Summary
The decline of third-party cookies will result in significant changes to digital marketing. Businesses will need to explore different approaches to reach potential customers, collect more data directly from their own website or offline, prioritise gaining explicit consent from users, and modify their methods for measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
This shift towards first-party tracking aligns with the growing emphasis on user privacy and data protection and provides an opportunity for businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers. Therefore, businesses will need to adjust their strategies accordingly and focus on gathering first-party data to succeed in the changing landscape of digital marketing. Companies will need to emphasise gathering first-party data such as email addresses from potential customers and utilise it effectively to guide them through the various stages of purchasing a product or service.
CRM systems with advanced marketing features for lead nurturing and feeding data back to ad platforms will be a game changer for early adopters.
Google Chrome, the most widely used web browser globally, will soon stop supporting third-party cookies, making it harder for businesses to track user behaviour and gather data for advertising purposes.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is designed to emphasise first-party tracking rather than third-party tracking, allowing businesses to collect first-party data directly from their own website or app.
Server Event Tracking & 1st Party Data Encryption: Companies are already using this as an alternative to the standard tracking scripts like Google Tag Manager.
Although these changes may present challenges, they also provide opportunities for innovation and creativity in the digital marketing industry. Ultimately, businesses that can adapt to these new challenges and use innovative ways to connect with their customers will have a greater chance of long-term success.
Want to learn more about using a CRM for advertising and offline Conversion tracking?